Convolutional Neural Networks
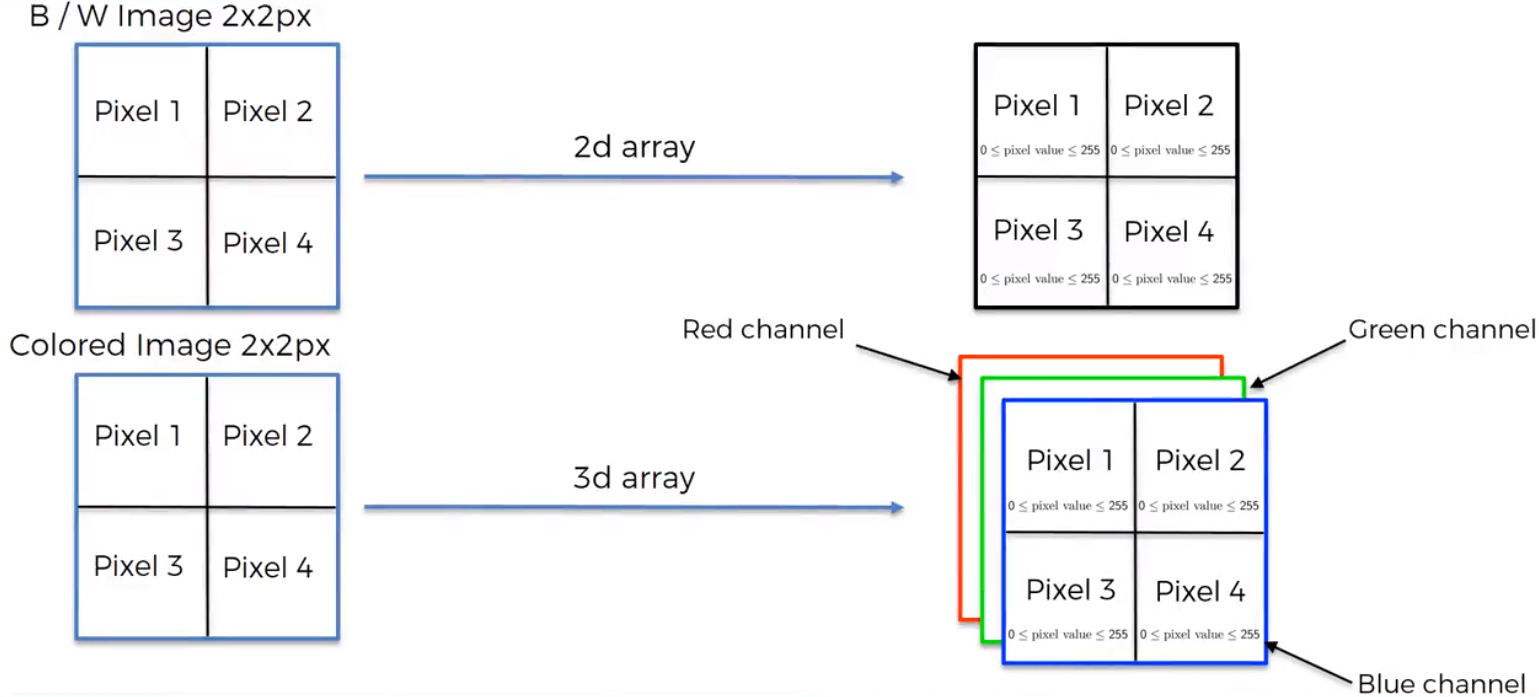
Image breakdown is what computers do to make sense of images. This requires taking each pixel inn an image and using color scale value to create an array. In the case of black and white images each pixel is given a value of 0 to 255 (255 representing white, 0 being black and everything in between being grey). For a colored image, we form 3-dimensional array with a red, green, and blue layer with each layer having its own specific value between 0 to 255.
A trivial example, like the one shown below will help us understand why computers break information down this way.
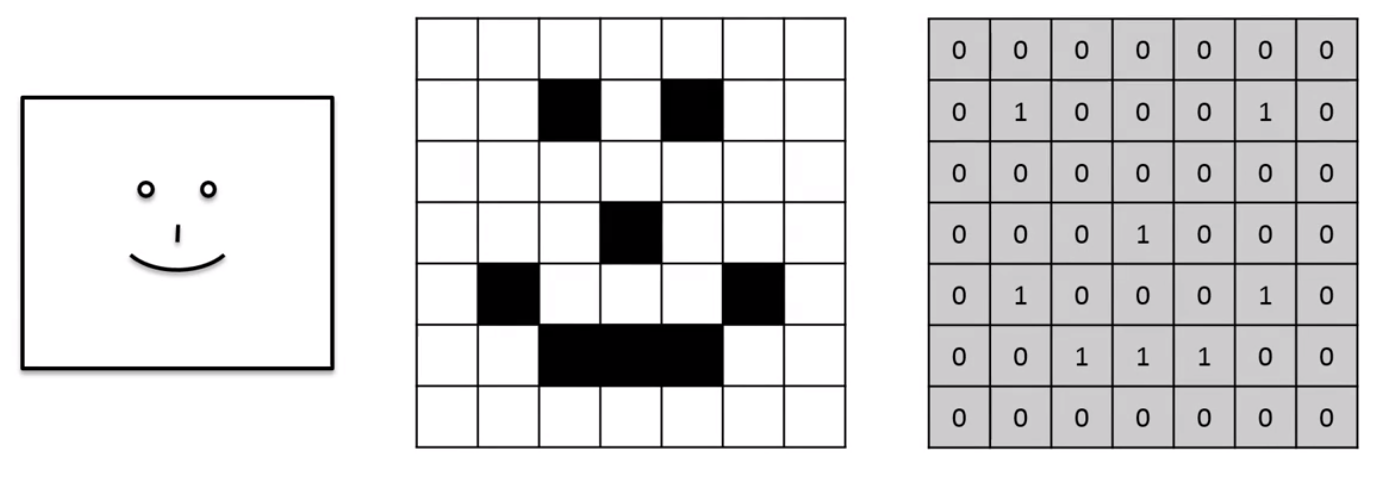
Here we have 0 representing white and 1 black, giving us the following array. We could then tell the computer, “Hey when you see this array is an image it means someone is smiling”. This is called feature detection. Using information, we gathered from training, we search for these features in images to try and detect whether the target feature is present or not.
Convolution
Essentially it is the combined integration of two functions. With on function modifying the shape of the other, as seen below.
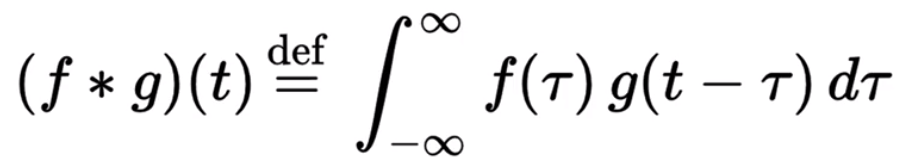
Read: Introduction to convolutional Neural Networks By Jianxin Wu
Some more useful for this dude:
So, convolution start by having two arrays. The first is the image array and the second being the Feature Detector Array (usually 3x3 matrix but it can be any size really) (other names: Kernel or Filter). The x in the circle signifies the convolution operation.
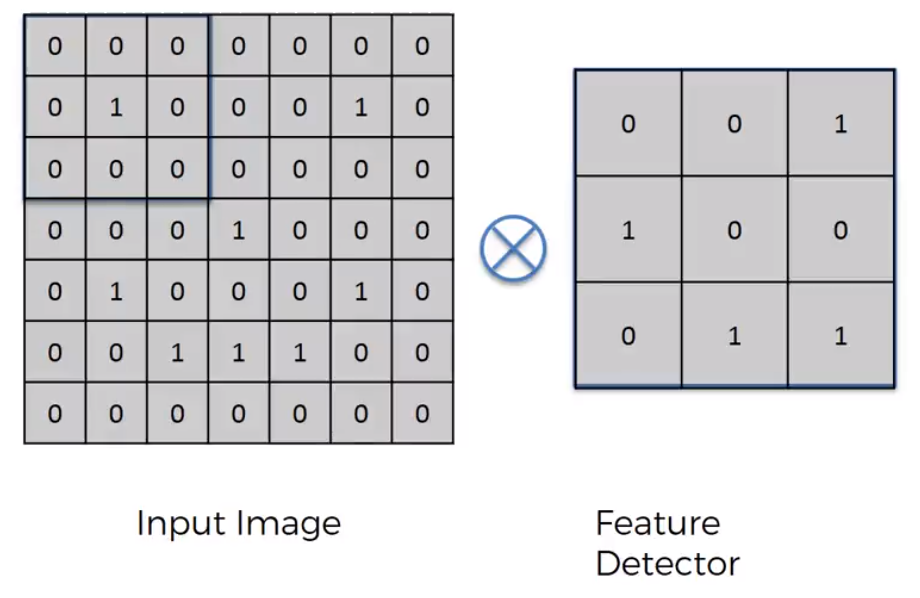
On an intuitive level how, it works is by placing the feature detector over the input image and moving left to right, top to bottom. Each respected value is (top left on the area of the Input image that we are currently looking at and top left on Feature Detector) are multiplied together and then added up. The result is recorded onto the Feature Map.
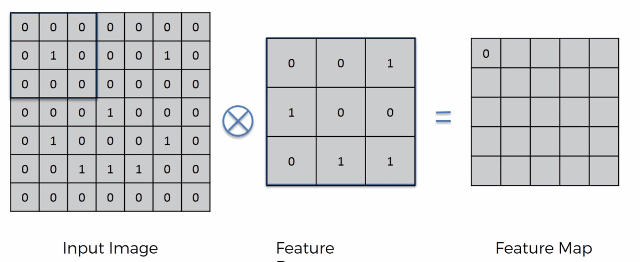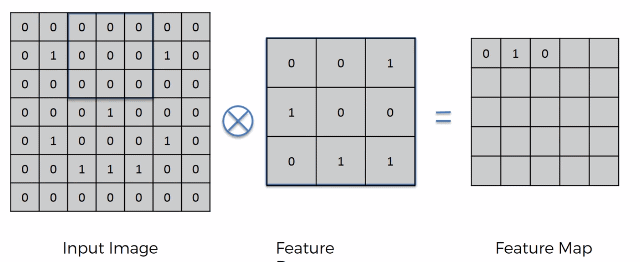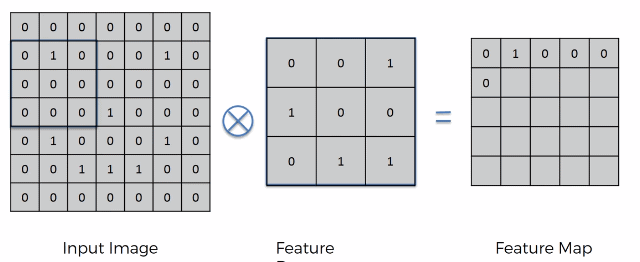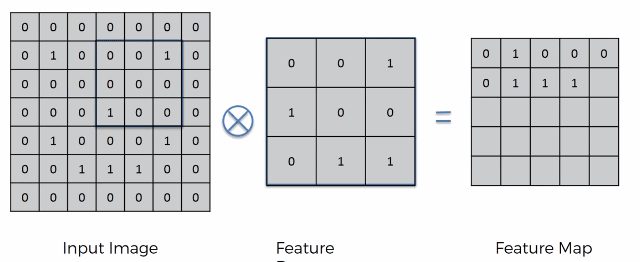
The step at we move is called a stride. In this case we have a stride of 1 pixel.
The Feature Map (or Convolved Feature / Activation Map). You can think of the feature map as a compressed version of the image. This compression makes it much easier to do calculations on the feature map later. Here we had a stride of 1, by having a lot of strides we further compress in the image increasing process speed but also reducing the amount of data in the image. The reduction in data however is not completely bad, since remember we only care about the detection of important features. The rest of the image is essentially meaningless. The Feature Map helps us preserve this important data. By applying more and more Feature Detectors on a certain input image we create a set of Feature Maps called the Convolutional Layer.
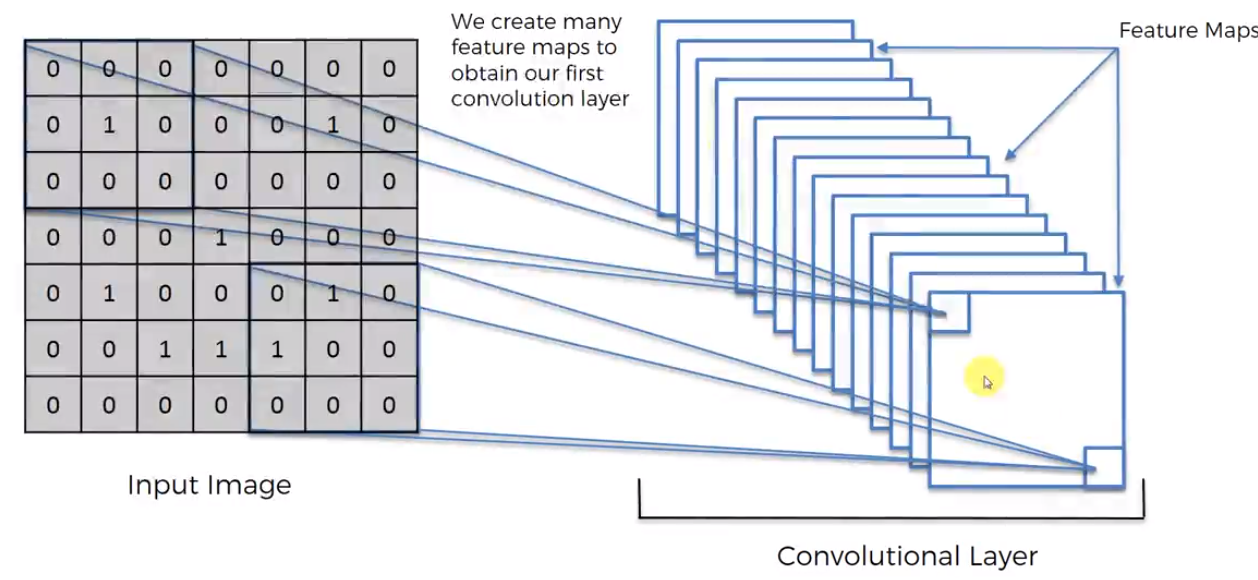
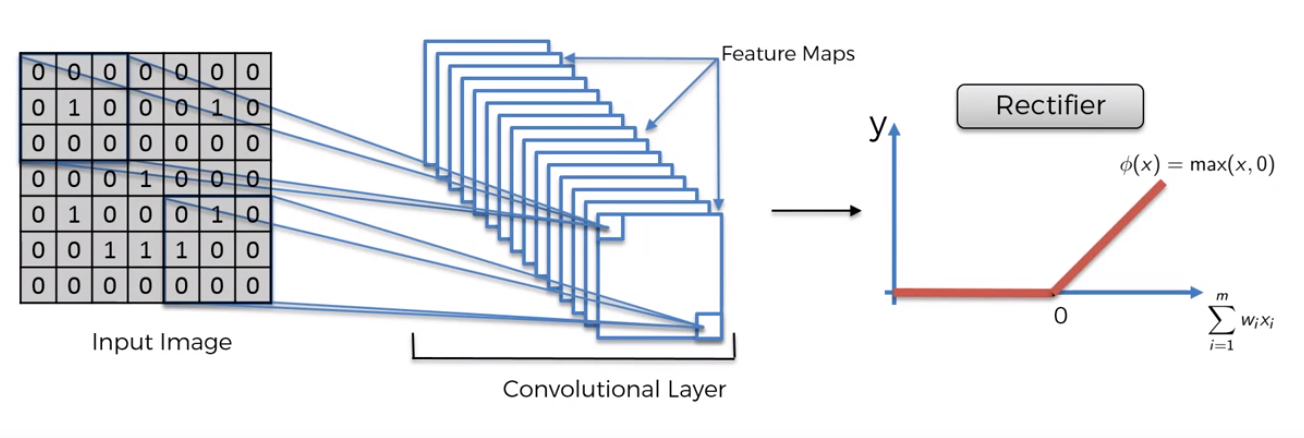
ReLU Layer (Rectified Linear Units Layer)
This is the application of the Rectifier function on the Convolutional Layer. The reason we want to do this is because we want to increase non-linearity in our convolutional neural network, since images are highly non-linear, and we want this feature to be preserved when processing it. When building our Convolutional Layer we risk the potential for linearity, the Rectifier Function acts as a filter to ensure this does not happen.
Some resources:
Understanding Convolutional Neural Networks with A Mathematical Model
[Delving Deep into Rectifiers: Surpassing Human-Level Performance on ImageNet Classification] (https://arxiv.org/pdf/1502.01852.pdf)
Max Pooling
Spatial Variance – The neural network should not take into consideration if features are closer together, further apart, stretched, squished, etc relative to each other.
How Max pooling works:
We take our Feature Map and looking at a subsection of the Feature Map we take the largest value from that subsection and use it to generate a new array called Pooled Feature Map.
Move the subsection by a certain stride, here it’s 2.
Repeat until the Pooled Feature Map is created.

What does this do:
- Further removes unnecessary data (reducing size, in this case 75%)
- By taking the max value, we account for distortions, by a certain degree.
- Preserves most necessary features
- Prevents overfitting.
Evaluation of Pooling Operations in Convolutional Architectures for Object Recognition
Flattening
Flattening is simply just converting our 2d array into a one-dimensional array, by taking each value row by row.
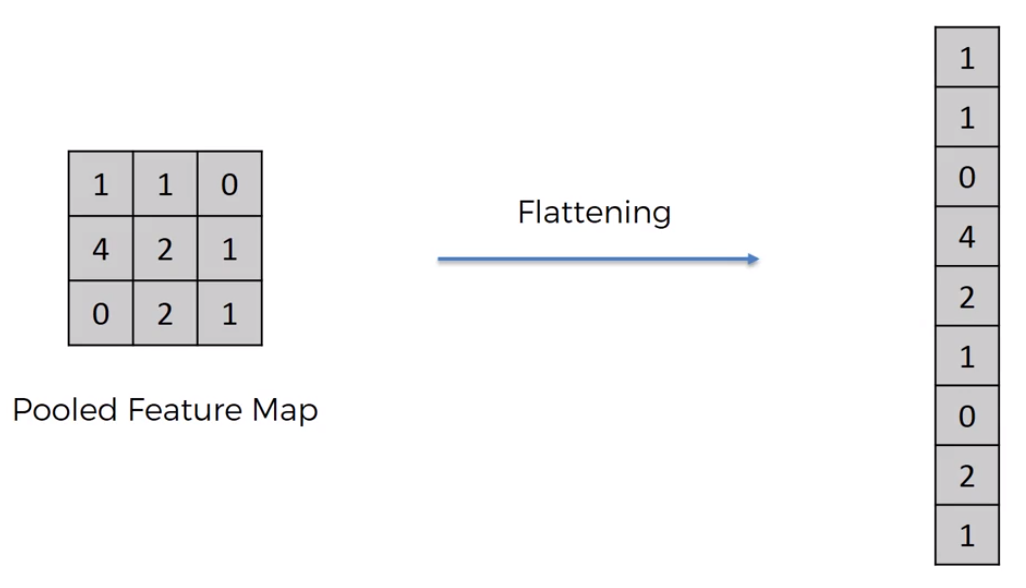
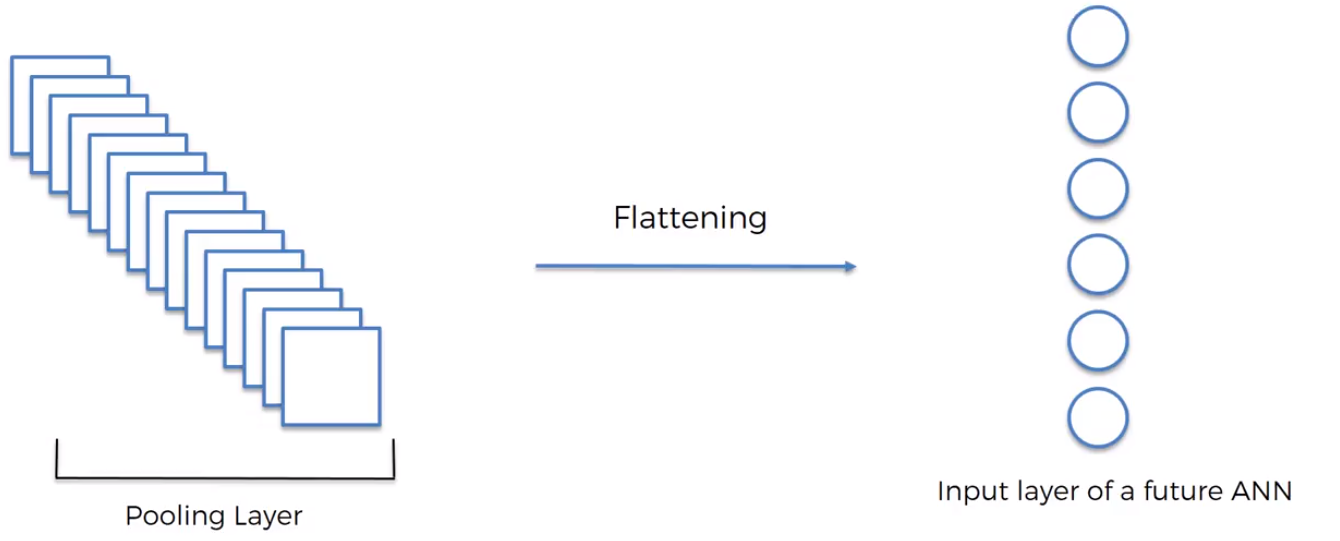
This is then going to be used as individual inputs when we process it through our artificial neural network.
Full Connection
So once all the previous steps are complete we add the backbone which is the artificial neural network. We know from previously that our flattened input layer already has enough distinct feature detections to do an accurate job of classifying a new image but with an ANN we could do far better. The ANN can be used to combine attributes or even find new attributes present in images to further predict whether an image is whatever we’re looking for. This happens by modifying the feature detector as well as weights on the ANN.
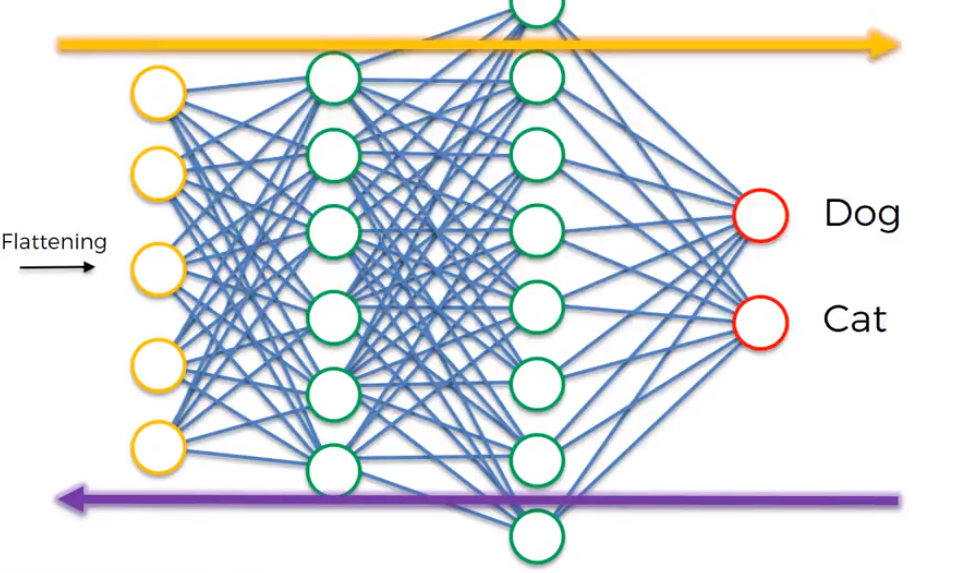
A fully connected layer is essentially just a hidden layer that is fully connected to every input layer.
Softmax Function
So, in reality when trying to get prediction values for two or more classifications, there is no way for the two output layers to know what the value of the other neuron so that the summation of their values adds up to one. Obviously, this is important because we don’t want our prediction to say that there is a 0.9 probability value that the image is a dog and 0.8 value that it’s a cat. To get around this issue we use the softmax function.
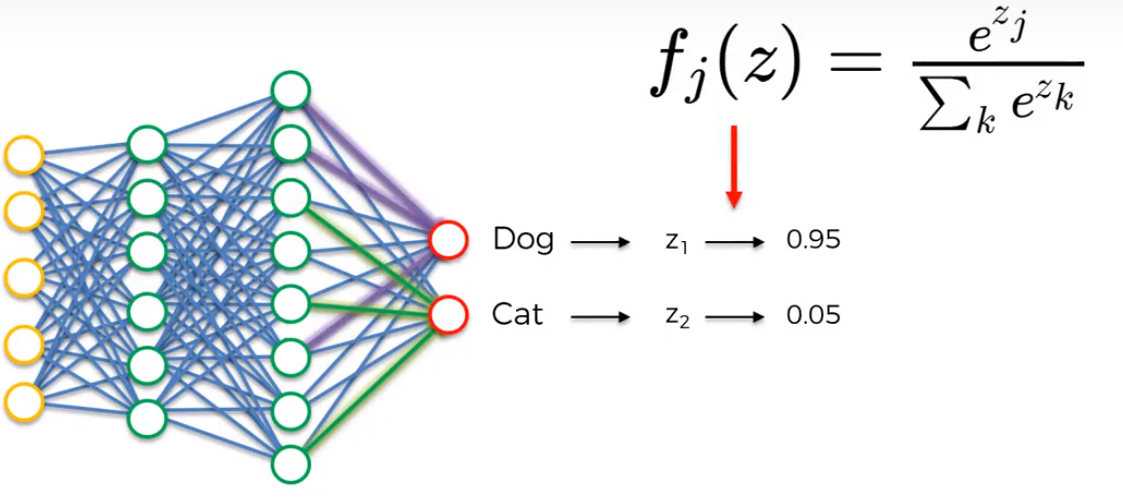
What the softmax function does is that it will convert the value predictions to be between 0 and 1.
Cross Entropy Function
[Image]
A cross entropy function is used in a similar manner as the cost function used in ANN’s, and is called the Loss Function. The goal being to minimize this value to maximize performance.
[Image]
Here on the right side is the two classifications (1 = Dog and 0 = Cat).
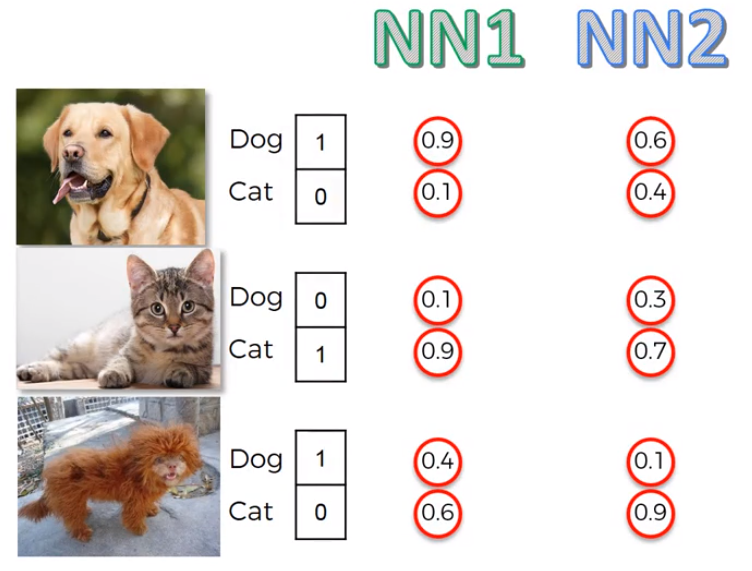
Another Example looking at two competing neural networks
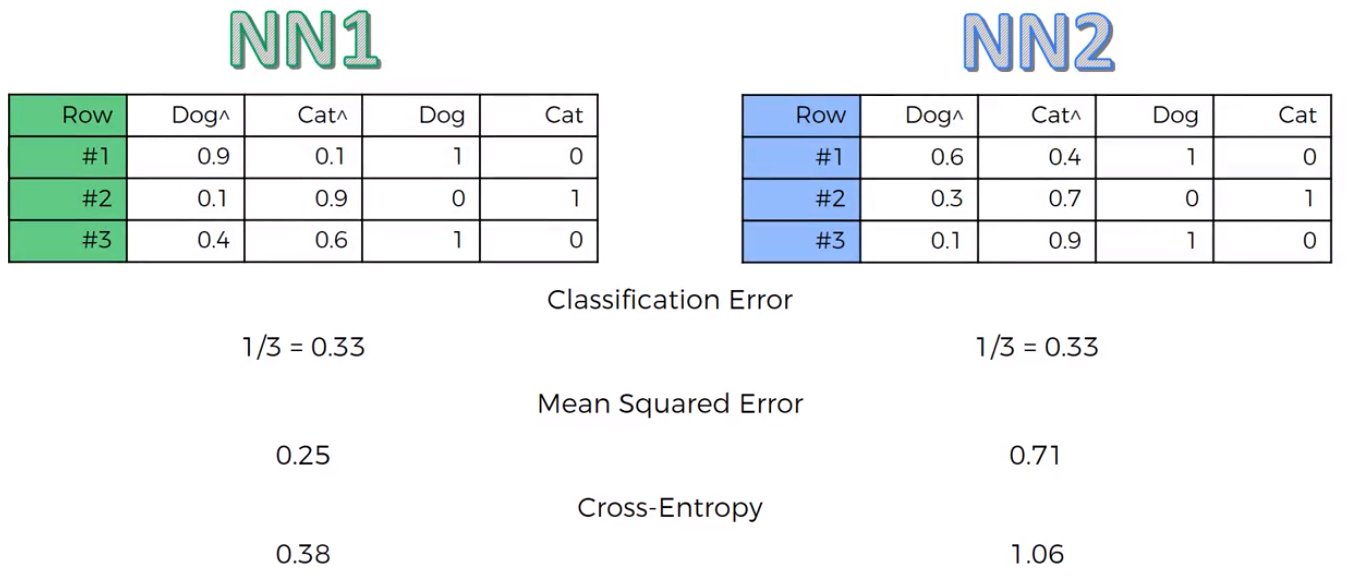
Here we see that NN1 outperforms NN2 much more and looking at the Cross-Entropy values we see that the value for NN1 is much lower.